🧠 Test Your Knowledge!
Structure of the Earth » Introduction to Earth as a Planet
What you'll learn this session
Study time: 30 minutes
- Understand Earth's position in the solar system and its unique characteristics
- Learn about Earth's basic structure and composition
- Explore the formation and age of our planet
- Discover what makes Earth suitable for life
- Examine Earth's layers and their properties
- Understand the importance of Earth's magnetic field and atmosphere
Introduction to Earth as a Planet
Welcome to the fascinating world of Earth science! Our planet is truly remarkable - it's the only known place in the universe where life exists. But what makes Earth so special? In this session, we'll explore Earth's unique position in space, its structure and the incredible processes that have shaped our home for billions of years.
Earth isn't just a big rock floating in space. It's a dynamic, living system with layers, cycles and processes that work together to create the perfect conditions for life. From its molten core to its protective atmosphere, every part of Earth plays a crucial role in making our planet habitable.
Key Definitions:
- Planet: A large celestial body that orbits a star and has cleared its orbital path of other objects.
- Solar System: The collection of planets, moons, asteroids and comets that orbit our Sun.
- Terrestrial Planet: A rocky planet with a solid surface, like Earth, Mars, Venus and Mercury.
- Atmosphere: The layer of gases surrounding a planet, held in place by gravity.
- Magnetic Field: An invisible force field around Earth that protects us from harmful solar radiation.
🌍 Earth's Place in Space
Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system. It sits in what scientists call the "Goldilocks Zone" - not too hot, not too cold, but just right for liquid water to exist. This perfect distance from the Sun means Earth receives just the right amount of energy to support life as we know it.
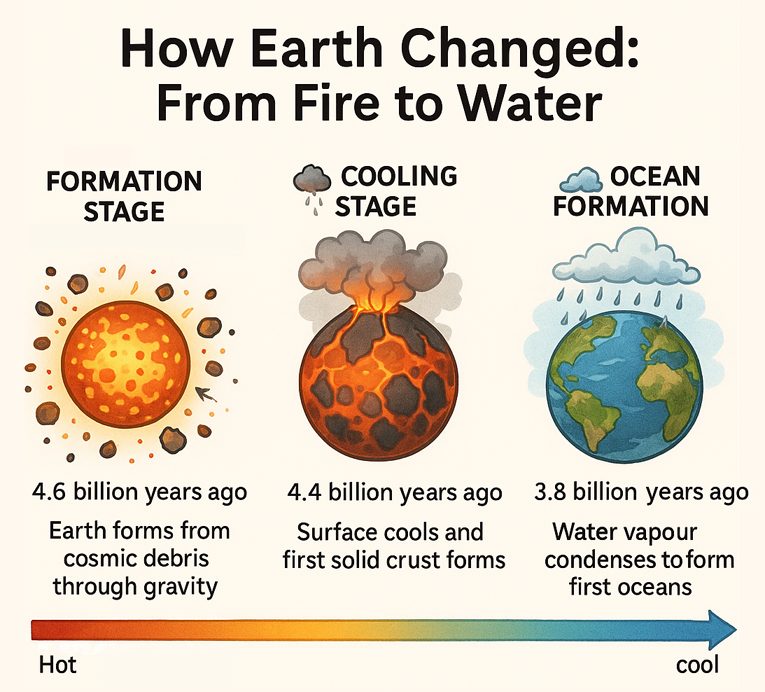
Formation and Age of Earth
Our planet formed approximately 4.6 billion years ago through a process called accretion. Imagine billions of space rocks, dust and gas slowly clumping together under the force of gravity. As these materials collided and stuck together, they generated enormous heat, eventually forming the molten ball that would become Earth.
The Early Earth Story
The young Earth was nothing like the planet we know today. It was a hellish world of molten rock, constant volcanic eruptions and a toxic atmosphere. There was no oxygen to breathe, no oceans and certainly no life. The surface was so hot that rocks melted like butter!
🔥 Formation Stage
4.6 billion years ago - Earth forms from cosmic debris and dust through gravitational attraction.
🌊 Cooling Stage
4.4 billion years ago - Earth's surface begins to cool and solidify, forming the first solid crust.
🌊 Ocean Formation
3.8 billion years ago - Water vapour condenses to form the first oceans as temperatures drop.
Amazing Earth Facts
Did you know that Earth is the densest planet in our solar system? It's also the only planet not named after a Greek or Roman god - the name "Earth" comes from Old English and Germanic words meaning "ground" or "soil". Our planet spins at about 1,670 kilometres per hour at the equator, yet we don't feel this incredible speed!
Earth's Unique Characteristics
What makes Earth so special compared to other planets? Several key factors work together to create the perfect conditions for life. Let's explore these remarkable features that make our planet truly one-of-a-kind in the known universe.
The Goldilocks Conditions
Earth's distance from the Sun creates what scientists call the "habitable zone." This means our planet receives just the right amount of solar energy - not too much (like Venus) and not too little (like Mars). This perfect balance allows water to exist in all three states: solid ice, liquid water and water vapour.
🌡 Perfect Temperature Range
Earth's average temperature is about 15°C, which allows liquid water to exist on the surface. This temperature range is maintained by our atmosphere, which acts like a blanket, trapping just enough heat to keep us warm but not too much to make us overheat.
Earth's Structure and Layers
Think of Earth like a giant onion with different layers. Each layer has its own unique properties, temperature and composition. Understanding these layers helps us understand how our planet works and why certain processes occur.
The Four Main Layers
Earth consists of four main layers, each with distinct characteristics. From the outside in, these are the crust, mantle, outer core and inner core. The deeper you go, the hotter and denser it becomes!
🌏 The Crust
The thin outer shell where we live. It's only 5-70 km thick - thinner than an apple's skin compared to the whole apple!
🔥 The Mantle
The thickest layer, made of hot, semi-solid rock. It's about 2,900 km thick and reaches temperatures of 3,700°C.
🔥 The Core
Split into outer (liquid) and inner (solid) parts. Made mostly of iron and nickel, reaching 6,000°C - hotter than the Sun's surface!
Case Study Focus: Earth's Magnetic Shield
Earth's magnetic field is generated by the movement of molten iron in the outer core. This invisible shield protects us from harmful solar radiation and cosmic rays. Without it, our atmosphere would be stripped away by solar winds, just like what happened to Mars billions of years ago. The magnetic field also creates the beautiful aurora (Northern and Southern Lights) when solar particles interact with our atmosphere near the poles.
Earth's Protective Systems
Our planet has several built-in protection systems that make life possible. These natural shields and cycles work together to create a stable, habitable environment that has supported life for billions of years.
The Atmosphere - Our Protective Blanket
Earth's atmosphere is like a protective bubble around our planet. It's made up of 78% nitrogen, 21% oxygen and 1% other gases. This mixture is perfect for life - the oxygen we breathe and the nitrogen that helps plants grow.
🌪 Atmospheric Protection
Our atmosphere protects us in many ways: it burns up most meteors before they reach the ground, filters out harmful radiation from space and maintains stable temperatures through the greenhouse effect. Without our atmosphere, Earth would be a frozen, lifeless rock with temperatures swinging from +120°C to -170°C!
Earth's Dynamic Processes
Earth is constantly changing through various processes. These changes happen on different timescales - some take millions of years, while others happen in seconds. Understanding these processes helps us appreciate how dynamic and alive our planet really is.
The Rock Cycle and Plate Tectonics
Earth's surface is made up of massive pieces called tectonic plates that slowly move around like puzzle pieces on a conveyor belt. This movement creates mountains, causes earthquakes and forms new ocean floor. It's like Earth is constantly recycling itself!
🌋 Mountain Building
When plates collide, they push up massive mountain ranges like the Himalayas, which are still growing today!
🌌 Ocean Formation
When plates pull apart, they create new ocean floor and can form new seas and oceans over millions of years.
🌋 Volcanic Activity
Plate boundaries are where most volcanoes form, creating new land and recycling old rocks back into the mantle.
Earth's Water Cycle - The Ultimate Recycling System
Every drop of water on Earth has been recycled countless times through the water cycle. The water you drink today might have once been part of a dinosaur, fallen as rain on ancient civilizations, or frozen in glaciers for thousands of years. This continuous cycle of evaporation, condensation and precipitation has been operating for billions of years, distributing fresh water around the globe and helping to regulate Earth's temperature.
Why Earth is Perfect for Life
The combination of all these factors - the right distance from the Sun, a protective atmosphere, liquid water, a magnetic field and dynamic geological processes - creates the perfect recipe for life. Earth is like a carefully balanced ecosystem where everything works together in harmony.
The Goldilocks Planet
Scientists often call Earth the "Goldilocks Planet" because everything is "just right" for life. This perfect balance has allowed life to not only survive but to thrive and evolve into the incredible diversity we see today. From tiny bacteria to massive whales, from deep-sea creatures to high-altitude birds, life has adapted to almost every environment on Earth.
Access the full course and all the resources like custom timetables and progress tracking.
Join Today