Introduction to Business Ownership Structures
When starting a business, one of the most important decisions entrepreneurs face is choosing the right form of ownership. This choice affects everything from how much tax you pay to how much personal risk you take on. Different ownership structures suit different types of businesses and what works for a corner shop might not work for a tech startup.
The form of ownership you choose will determine your legal responsibilities, financial obligations and how much control you have over your business. It's a bit like choosing the right vehicle for a journey - you wouldn't use a bicycle to move house and you wouldn't use a lorry for a quick trip to the shops!
Key Definitions:
- Sole Trader: A business owned and run by one person who takes all profits and bears all losses.
- Partnership: A business owned by two or more people who share profits, losses and responsibilities.
- Private Limited Company (Ltd): A business owned by shareholders with limited liability, shares cannot be sold to the public.
- Public Limited Company (PLC): A company that can sell shares to the general public on the stock exchange.
- Limited Liability: Protection for owners where they can only lose the money they invested in the business.
- Unlimited Liability: Where business owners are personally responsible for all business debts.
👤 Sole Trader
The simplest form of business ownership. You're the boss, you make all decisions and you keep all profits. However, you're also responsible for all debts and losses. Perfect for small businesses like hairdressers, plumbers, or freelance designers.
Sole Traders - Going It Alone
Sole traders are the most common type of business in the UK. They're easy to set up - you just need to register with HMRC for tax purposes. Many successful businesses started as sole traders, including famous brands like Dyson and The Body Shop.
Advantages of Being a Sole Trader
Being a sole trader offers several benefits that make it attractive to new entrepreneurs:
⚡ Quick Setup
No complicated paperwork or legal requirements. You can start trading immediately after registering with HMRC.
💰 Keep All Profits
Every penny the business makes (after tax) goes straight into your pocket. No need to share with partners or shareholders.
🔨 Complete Control
You make all decisions about the business direction, products and services. No need to consult anyone else.
Disadvantages of Being a Sole Trader
However, going it alone also comes with significant risks:
⚠ Unlimited Liability
If the business fails, you could lose your personal assets like your house or car to pay business debts.
💤 Limited Resources
Raising money for expansion can be difficult as banks are often reluctant to lend to sole traders.
😷 Work Pressure
You're responsible for everything - if you're ill or on holiday, the business stops. This can lead to stress and burnout.
Case Study Focus: James Dyson - From Sole Trader to Global Brand
James Dyson started as a sole trader in 1978, developing his revolutionary vacuum cleaner design. He spent 15 years and created 5,126 prototypes before finding success. Starting as a sole trader allowed him complete control over his invention, but he later formed a limited company to protect his personal assets and raise capital for manufacturing. Today, Dyson Ltd is worth billions and employs thousands worldwide.
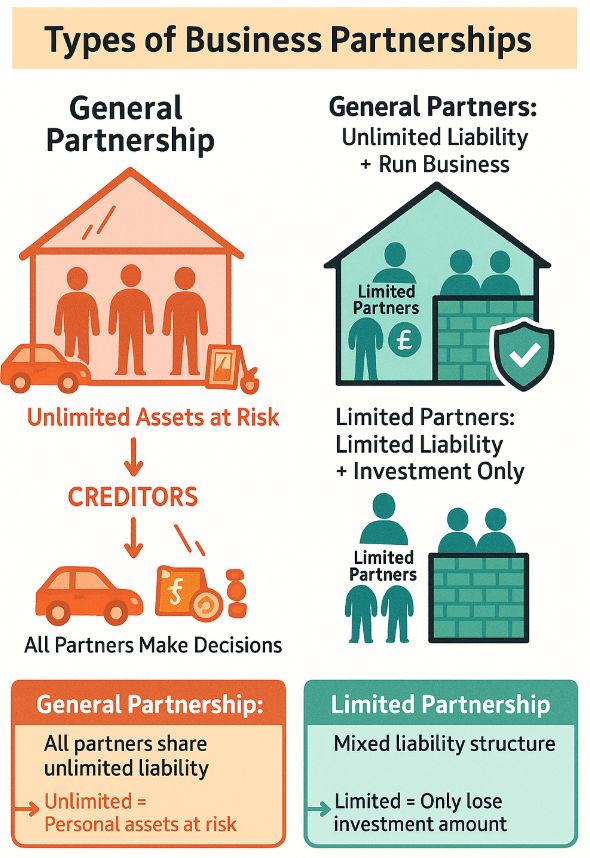
Partnerships - Sharing the Load
Partnerships involve two or more people running a business together. They share the workload, costs and profits. Think of famous partnerships like Ben & Jerry's ice cream or the law firms you see on every high street.
Types of Partnerships
There are different types of partnerships to consider:
🤝 Ordinary Partnership
All partners share profits, losses and have unlimited liability. Most common type of partnership, often used by professionals like doctors, lawyers and accountants.
🛡 Limited Partnership
Some partners have limited liability (sleeping partners) while others have unlimited liability (active partners). Less common but useful when some partners just want to invest money.
Partnership Advantages and Disadvantages
Partnerships offer a middle ground between sole traders and companies:
💪 Shared Expertise
Partners can bring different skills - one might be great at sales while another excels at finance.
💲 More Capital
Multiple partners can contribute more money to start and grow the business.
🤝 Shared Risk
Business responsibilities and stress are shared among partners.
Case Study Focus: Ben & Jerry's Partnership Success
Ben Cohen and Jerry Greenfield started their ice cream business as a partnership in 1978 with just $12,000. Their different skills complemented each other perfectly - Ben handled the business side while Jerry focused on the product. Their partnership agreement was crucial in defining roles and profit-sharing. The company grew from a single shop to a global brand, eventually selling to Unilever for $326 million.
Limited Companies - Protection and Growth
Limited companies are separate legal entities from their owners. This means the company can own assets, enter contracts and be sued independently of its shareholders. It's like creating a legal 'person' that exists separately from you.
Private Limited Companies (Ltd)
Private limited companies cannot sell shares to the general public. They're perfect for family businesses or small companies that want limited liability protection.
🛡 Limited Liability
Shareholders can only lose the money they invested. Personal assets are protected if the business fails.
📈 Professional Image
Having 'Ltd' after your name makes the business appear more established and trustworthy to customers and suppliers.
💰 Tax Advantages
Corporation tax rates are often lower than income tax rates, potentially saving money as the business grows.
Public Limited Companies (PLC)
PLCs can sell shares to the public through the stock exchange. This allows them to raise large amounts of capital but comes with strict regulations and reporting requirements.
🏦 When to Choose Each Structure
Sole Trader: Perfect for small, low-risk businesses like freelancers, consultants, or local services. Choose this if you want simplicity and complete control.
Partnership: Ideal when you need complementary skills or more capital than you can provide alone. Great for professional services.
Ltd Company: Best for businesses with higher risks, those planning to grow significantly, or when you want to protect personal assets.
PLC: Only suitable for large businesses needing substantial capital investment from the public.
Factors Affecting Choice of Ownership
Choosing the right ownership structure depends on several key factors that every entrepreneur must consider carefully.
Key Decision Factors
When deciding on business ownership structure, consider these crucial elements:
⚠ Risk Level
High-risk businesses (manufacturing, construction) often choose limited companies for protection. Low-risk services might stay as sole traders.
💰 Capital Needs
Businesses needing lots of startup money often choose partnerships or companies to access more funding sources.
📈 Growth Plans
If you plan to expand rapidly, a limited company structure makes it easier to bring in investors and grow.
Case Study Focus: Innocent Drinks - Evolution of Ownership
Innocent Drinks started as a partnership between three Cambridge graduates in 1999. They began by testing their smoothie idea at a music festival with a simple sign: "Should we give up our jobs to make these smoothies?" As the business grew and needed investment, they converted to a limited company. This allowed them to bring in investors like Coca-Cola while protecting their personal assets. The company sold to Coca-Cola for over £300 million, showing how the right ownership structure can facilitate growth and eventual exit strategies.
Making the Right Choice
The appropriateness of different forms of ownership isn't just about what works now - it's about what will work as your business evolves. Many successful businesses start as sole traders and evolve into limited companies as they grow.
Remember, you can change your business structure as circumstances change. What matters most is choosing the structure that best fits your current situation while keeping future growth in mind. The key is understanding the trade-offs between simplicity, control, risk and growth potential.
Consider seeking professional advice from accountants or business advisors when making this crucial decision. The right choice of ownership structure can be the foundation for business success, while the wrong choice can create unnecessary complications and costs.