Loss of Cultural Identity Through Tourism
Tourism brings people from different cultures together, which can have both positive and negative effects on local communities. When tourists visit destinations, they bring their own cultural values, behaviours and expectations, which can influence local people and traditions.
Key Definitions:
- Cultural Identity: The characteristics, traditions, customs and beliefs that make a particular group of people distinct from others.
- Loss of Identity: When traditional cultures, customs or ways of life are diluted, changed or abandoned due to outside influences.
- Demonstration Effect: When local people observe and then adopt the behaviours, attitudes and spending patterns of tourists.
🌍 How Tourism Can Affect Cultural Identity
Tourism can lead to changes in local traditions, values and lifestyles in several ways:
- Local customs being modified to meet tourist expectations
- Traditional ceremonies becoming performances for tourists
- Local arts and crafts changing to appeal to tourist tastes
- Languages being diluted as English becomes more widely used
- Traditional clothing being replaced by Western styles
- Changes in family structures and community relationships
🏳️ Signs of Cultural Identity Loss
You can spot cultural identity loss when:
- Traditional festivals lose their original meaning
- Local foods are adapted to suit foreign tastes
- Religious practices become less important
- Traditional skills and crafts are forgotten
- Historic buildings are repurposed for tourism
- Local communities move away from tourist areas
Understanding the Demonstration Effect
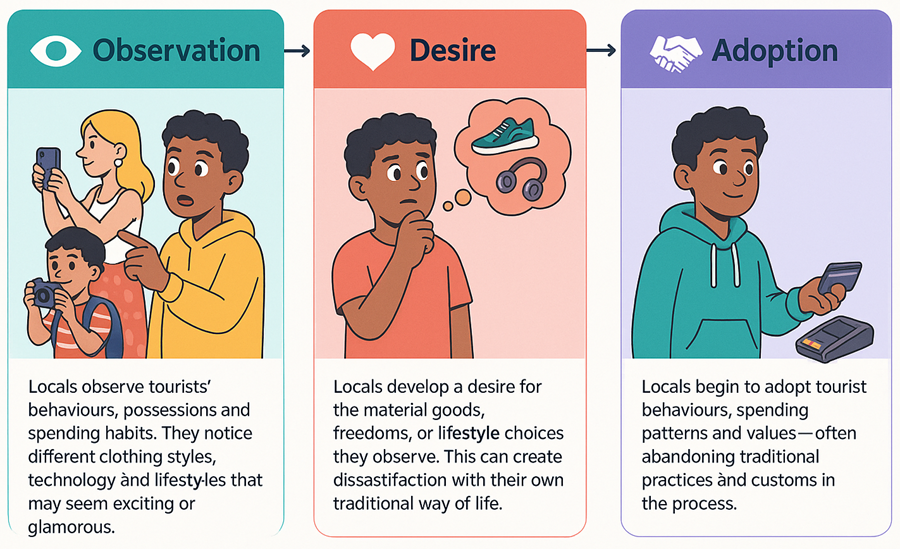
The demonstration effect is particularly noticeable among young people in tourist destinations. As they observe visitors with different lifestyles, clothing, technology and spending habits, they often begin to imitate these behaviours.
How the Demonstration Effect Works
The demonstration effect typically follows this pattern:
Positive and Negative Impacts of the Demonstration Effect
🌟 Potential Benefits
- Increased awareness of global issues
- Adoption of beneficial practices (e.g., improved hygiene)
- Greater educational and career aspirations
- Increased entrepreneurial spirit
- Reduced harmful traditional practices
- Improved status of women in some societies
⚠️ Potential Problems
- Abandonment of traditional values and customs
- Increased materialism and consumerism
- Growing economic inequality within communities
- Resentment when desired lifestyles are unattainable
- Increased crime as people seek ways to afford new lifestyles
- Breakdown of family and community structures
Commercialisation of Culture
One of the most visible impacts of tourism on cultural identity is the commercialisation of local traditions and customs. As destinations seek to attract tourists, cultural elements are often packaged and presented as products or experiences.
How Cultural Elements Become Tourist Products
Traditional aspects of culture are often modified to meet tourist expectations:
- Shortened ceremonies: Religious or cultural rituals may be condensed to fit tourist schedules
- Simplified crafts: Traditional crafts may be mass-produced or simplified for quick sale
- Staged authenticity: Cultural experiences that appear authentic but are actually created specifically for tourists
- Commodification: Sacred or meaningful cultural elements become products with price tags
- Cultural performances: Traditional dances or music performed out of context for entertainment
Case Study Focus: Maasai Tribe, Kenya and Tanzania
The Maasai people have experienced significant cultural impacts from tourism:
- Traditional villages have been transformed into "cultural villages" where tourists pay to take photos
- Sacred ceremonies like warrior dances are now regular performances for tourists
- Many young Maasai have abandoned traditional herding to work in tourism
- Traditional beadwork and crafts have been adapted to tourist preferences
- Some Maasai now wear traditional clothing only when tourists visit, switching to Western clothes otherwise
While tourism has provided income, it has also led to a dilution of authentic Maasai culture and created divisions between those who benefit from tourism and those who don't.
Real-World Examples of Cultural Identity Loss
🏝️ Balinese Culture, Indonesia
Bali has experienced significant cultural changes due to mass tourism:
- Sacred temple ceremonies are now advertised as tourist attractions
- Traditional dances have been shortened and modified for tourist entertainment
- Agricultural land has been converted to hotels and resorts
- Young Balinese increasingly adopt Western clothing and values
- Traditional family compounds are being replaced by modern housing
🛶 Venice, Italy
Venice shows how tourism can transform a living city:
- Local population has declined from 175,000 to about 50,000 since the 1950s
- Traditional shops have been replaced by souvenir stores and luxury brands
- Local crafts like Murano glass are now mass-produced or imported
- Housing prices have forced locals out as properties become holiday rentals
- Traditional Venetian cuisine has been modified to suit tourist tastes
Strategies to Minimise Negative Cultural Impacts
While tourism can threaten cultural identity, there are approaches that can help preserve local cultures while still allowing for tourism development:
Sustainable Cultural Tourism Approaches
- Community involvement: Ensuring local communities have control over how their culture is presented
- Education: Informing tourists about appropriate behaviour and cultural sensitivity
- Authentic experiences: Promoting genuine cultural exchanges rather than staged performances
- Limiting visitor numbers: Preventing overcrowding at cultural sites and events
- Supporting traditional crafts: Helping artisans maintain traditional methods and quality
- Cultural heritage protection: Legal frameworks to protect important traditions and sites
- Fair economic distribution: Ensuring tourism benefits reach local communities
Case Study: Bhutan's "High Value, Low Impact" Tourism
Bhutan has developed a unique approach to tourism that helps protect its cultural identity:
- All tourists must pay a daily fee of $200-$250, which includes a "sustainable development fee"
- Visitors must travel with licensed Bhutanese tour guides
- Tourism numbers are deliberately kept low to prevent overwhelming local communities
- Traditional architecture is legally protected and must be maintained
- Cultural events and religious festivals maintain their authenticity
- Tourism revenue directly funds education, healthcare and conservation
This approach has allowed Bhutan to develop tourism while maintaining its unique cultural identity and traditions.
Conclusion: Balancing Tourism and Cultural Preservation
The loss of cultural identity and the demonstration effect are significant challenges in tourism development. However, with careful planning and management, it's possible to develop tourism that respects and even strengthens local cultures rather than diminishing them.
The key is finding a balance that allows communities to benefit economically from tourism while maintaining control over how their culture is presented and experienced. When done right, tourism can actually help preserve cultural traditions by creating economic value for their continuation.
As you continue your studies, consider how different destinations are managing these challenges and what approaches seem most effective at protecting cultural identity while still allowing for tourism development.