Types of Tourists: A Comprehensive Review
Tourism is one of the world's largest industries, with people travelling for countless different reasons. Understanding the various types of tourists is essential for planning, marketing and managing tourism destinations effectively.
Key Definitions:
- Tourist: A person who travels to and stays in places outside their usual environment for leisure, business, or other purposes for at least one night but not more than one consecutive year.
- Excursionist: A visitor who does not stay overnight in the place visited (also called a day visitor).
- Domestic tourist: A resident of a country visiting destinations within their own country.
- International tourist: A person visiting a country other than their country of residence.
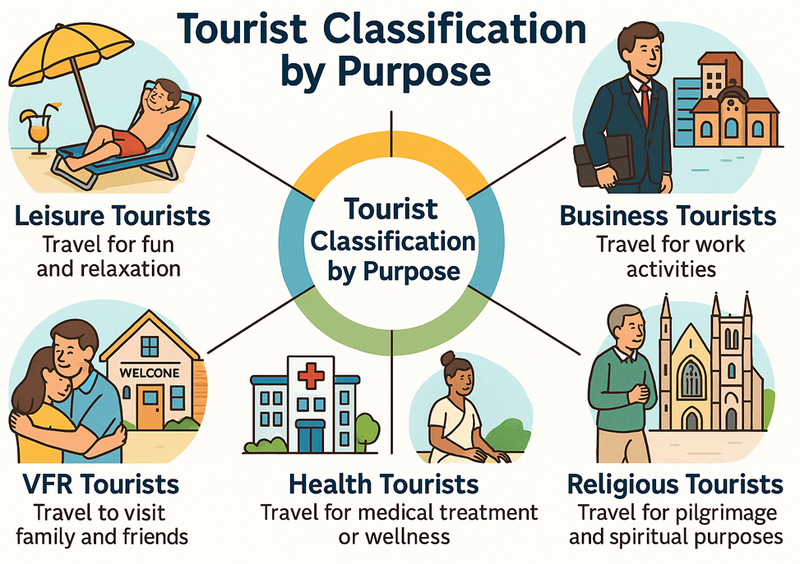
🎯 Classification by Purpose
Tourists can be classified based on their primary reason for travel:
- Leisure tourists: Travel for relaxation, recreation and enjoyment
- Business tourists: Travel for work-related activities
- Educational tourists: Travel for learning and study
- Religious tourists: Travel for pilgrimage or spiritual purposes
- Health tourists: Travel for medical treatment or wellness
- Visiting Friends and Relatives (VFR): Travel to see family or friends
🗺️ Classification by Destination
Tourists can also be categorised by where they travel to:
- Coastal tourists: Visit beaches and seaside locations
- Urban tourists: Visit cities and towns
- Rural tourists: Visit countryside and remote areas
- Mountain tourists: Visit highland and mountainous regions
- Cultural tourists: Visit heritage sites and cultural attractions
- Adventure tourists: Visit destinations for challenging activities
Understanding Tourist Behaviour
Different types of tourists have different needs, expectations and impacts on destinations. Understanding these differences helps tourism providers deliver appropriate services and manage impacts effectively.
👥 Mass Tourists
Characteristics:
- Travel in large groups
- Often on package holidays
- Prefer familiar environments
- Seek comfort and convenience
- Limited interaction with locals
Impact: High volume, concentrated in popular destinations, significant economic benefits but can cause overcrowding.
👤 Independent Tourists
Characteristics:
- Plan their own itineraries
- Seek authentic experiences
- More flexible travel plans
- Often budget-conscious
- Greater interaction with locals
Impact: More dispersed spending, may venture to less-visited areas, often more culturally sensitive.
🔍 Special Interest Tourists
Characteristics:
- Travel for specific activities
- Highly motivated by interests
- Often well-educated
- Willing to spend more
- Longer planning horizon
Impact: Higher spending per visitor, often support niche businesses, may help preserve cultural or natural heritage.
Tourist Typologies
Researchers have developed several models to categorise tourists based on their behaviour and motivations. These typologies help us understand the psychological and social aspects of tourism.
Cohen's Tourist Typology
Erik Cohen proposed a typology based on tourists' relationship with both their home environment and the host destination:
- Organised Mass Tourists: Least adventurous, remain in an "environmental bubble" of familiar surroundings, follow fixed itineraries with guides.
- Individual Mass Tourists: Similar to organised mass tourists but with more flexibility and occasional ventures outside the "bubble".
- Explorers: Arrange trips independently, try to get off the beaten track, but still look for comfortable accommodation and reliable transport.
- Drifters: Immerse themselves in local cultures, avoid tourist establishments, have no fixed itinerary and live with locals.
Plog's Psychographic Typology
Stanley Plog classified tourists along a spectrum from psychocentric to allocentric:
🏠 Psychocentrics (Dependables)
These tourists:
- Prefer familiar destinations
- Choose package holidays
- Enjoy relaxation and comfort
- Are less adventurous
- Prefer tourist areas and facilities
Example destinations: Blackpool, Costa del Sol, Benidorm
🌍 Allocentrics (Venturers)
These tourists:
- Seek new experiences and destinations
- Are adventurous and curious
- Enjoy meeting different people
- Make their own travel arrangements
- Require minimal tourist infrastructure
Example destinations: Remote parts of Nepal, Antarctica, undeveloped regions
Most tourists fall somewhere in the middle of this spectrum and are classified as "mid-centrics".
Emerging Tourist Types
The tourism industry is constantly evolving, with new types of tourists emerging in response to changing social values, technology and global challenges.
🌱 Sustainable Tourists
Increasingly conscious of their environmental impact, these tourists:
- Choose eco-friendly accommodations
- Support local businesses
- Minimise carbon footprint
- Respect local cultures and environments
- May participate in conservation activities
💻 Digital Nomads
Working remotely while travelling, these tourists:
- Stay in destinations for longer periods
- Need reliable internet and workspace
- Blend work and leisure activities
- Often become part of local communities
- Contribute to local economies over extended periods
Case Study Focus: Benidorm - Catering to Different Tourist Types
Benidorm in Spain has successfully evolved to attract various tourist types:
- Mass tourists: The city offers numerous high-rise hotels, package holidays and familiar food options that appeal to traditional mass tourists, particularly from the UK.
- Family tourists: Theme parks, water parks and family-friendly beaches cater to this segment.
- Senior tourists: Accessible facilities, mild winter climate and extended-stay options attract older visitors, especially during off-peak seasons.
- Special interest tourists: The surrounding mountains attract hikers and cyclists, while cultural events appeal to those interested in Spanish traditions.
By diversifying its offerings, Benidorm has reduced seasonality issues and created a more sustainable tourism model that can appeal to different market segments throughout the year.
Implications for Tourism Management
Understanding different tourist types helps destinations and businesses:
- Target marketing: Create tailored promotional materials for specific tourist segments
- Product development: Design appropriate facilities and experiences
- Impact management: Anticipate and mitigate potential negative effects
- Resource allocation: Invest in infrastructure that meets the needs of target tourists
- Visitor management: Develop strategies to handle different visitor behaviours
Key Assessment Points
When studying types of tourists for your iGCSE exam, remember to:
- Use correct terminology and definitions
- Provide specific examples to illustrate different tourist types
- Explain how tourist types influence destination development
- Consider both positive and negative impacts of different tourist types
- Link tourist typologies to real-world case studies
- Discuss how destinations can adapt to attract different market segments