Introduction to Island Destinations
Island destinations are among the most popular and iconic places for tourists around the world. From the tropical beaches of the Caribbean to the volcanic landscapes of Iceland, islands offer unique experiences that mainland destinations often cannot match.
Key Definitions:
- Island Destination: A piece of land completely surrounded by water that attracts tourists due to its unique geographical features, culture, or activities.
- Island Tourism: Travel activities that take place on islands, often focused on coastal attractions, unique ecosystems, or isolated cultures.
- Carrying Capacity: The maximum number of visitors an island can accommodate without causing environmental degradation or negative impacts on local communities.
🏝️ What Makes Islands Special?
Islands have distinct appeal as tourism destinations because they offer:
- Natural boundaries that create a sense of escape
- Unique ecosystems and biodiversity
- Often warmer climates (especially tropical islands)
- Distinctive cultural identities
- Water-based activities and pristine beaches
🗺️ Global Distribution
Island destinations can be found worldwide:
- Caribbean: Jamaica, Barbados, Bahamas
- Mediterranean: Cyprus, Malta, Ibiza
- Pacific: Fiji, Hawaii, Bali
- Indian Ocean: Maldives, Seychelles, Mauritius
- Northern Europe: Iceland, British Isles
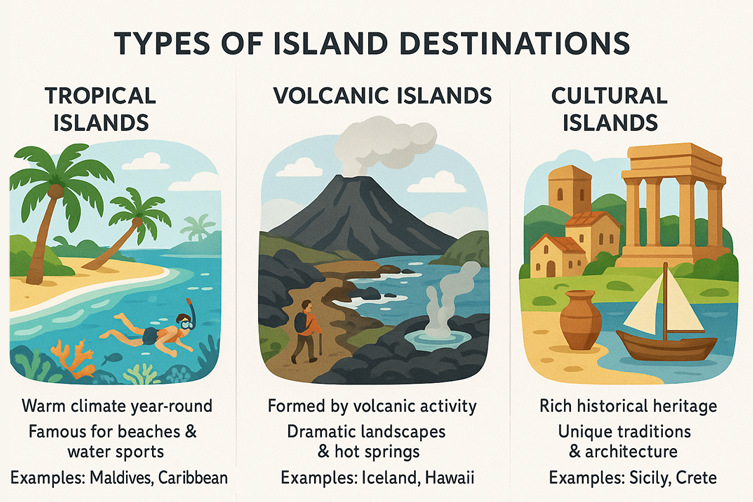
Types of Island Destinations
Islands come in many forms, each offering different tourism experiences and attractions. Understanding these categories helps us analyse why tourists choose certain island destinations over others.
🌴 Tropical Islands
Located near the equator with warm climates year-round. Famous for beaches, coral reefs and water sports.
Examples: Maldives, Seychelles, Caribbean islands
🌋 Volcanic Islands
Formed by volcanic activity, offering dramatic landscapes, hot springs and hiking opportunities.
Examples: Iceland, Hawaii, Santorini
🏛️ Cultural Islands
Islands with rich historical heritage, unique traditions and architectural attractions.
Examples: Sicily, Crete, Sri Lanka
Island Tourism Attractions
Islands offer a diverse range of attractions that appeal to different types of tourists. These attractions are often what drive tourism development and marketing strategies.
Natural Attractions
Islands often boast exceptional natural features that mainland destinations cannot match:
- Beaches: Often the primary draw for tourists, with white sand and clear waters
- Coral Reefs: Supporting snorkelling and diving tourism
- Unique Wildlife: Many islands have endemic species found nowhere else
- Dramatic Landscapes: Cliffs, volcanoes and unique geological formations
Cultural Attractions
The isolated nature of islands often leads to distinctive cultural development:
- Traditional Villages: Preserving ways of life that may have disappeared elsewhere
- Local Cuisine: Often based on seafood and unique local ingredients
- Festivals: Celebrations that maintain cultural traditions
- Crafts: Traditional skills passed down through generations
Case Study: The Maldives
The Maldives exemplifies successful luxury island tourism development:
- Consists of 26 atolls with about 1,190 islands in the Indian Ocean
- Tourism accounts for approximately 28% of GDP and 60% of foreign exchange earnings
- Pioneered the "one island, one resort" concept, where each resort occupies its own island
- Faces significant challenges from climate change and rising sea levels
- Has implemented sustainability initiatives including bans on single-use plastics and coral reef protection programmes
Economic Impacts of Island Tourism
Tourism often dominates the economies of island destinations, bringing both benefits and challenges:
💰 Positive Economic Impacts
- Job creation in hotels, restaurants and tour operations
- Foreign exchange earnings
- Infrastructure development (airports, roads, utilities)
- Entrepreneurial opportunities for locals
- Tax revenue for government services
📊 Economic Challenges
- Seasonal employment patterns
- Economic leakage when profits go to foreign companies
- Over-dependence on tourism making economies vulnerable
- Rising cost of living for locals
- Competition for resources (water, land, electricity)
Sustainability Challenges for Island Destinations
Islands face unique sustainability challenges due to their limited resources, fragile ecosystems and often small populations:
Environmental Challenges
- Limited Fresh Water: Many islands struggle with water supply for both residents and tourists
- Waste Management: Limited space for landfills and waste processing facilities
- Habitat Destruction: Development of hotels and infrastructure can damage natural environments
- Climate Change: Rising sea levels threaten low-lying islands, while changing weather patterns affect tourism seasons
- Coral Reef Damage: From pollution, boat anchors and tourist activities
Socio-cultural Challenges
- Cultural Dilution: Traditional ways of life changing to accommodate tourism
- Overtourism: Too many visitors overwhelming local communities
- Housing Pressures: Property prices rising beyond what locals can afford
- Seasonal Population Fluctuations: Straining services during peak times
Case Study: Sustainable Tourism in Iceland
Iceland has implemented innovative approaches to manage its growing tourism industry:
- Tourist tax used to fund infrastructure and environmental protection
- Visitor management through timed entry at popular sites like the Blue Lagoon
- Promotion of off-season tourism to reduce seasonal pressure
- Strict environmental regulations for new tourism developments
- Education campaigns like "Iceland Academy" to teach tourists about responsible behaviour
Future Trends in Island Tourism
Island destinations are evolving to meet changing tourist demands and address sustainability concerns:
🌿 Eco-tourism
Growing focus on nature-based activities with minimal environmental impact. Islands are ideal for wildlife observation, hiking and sustainable marine activities.
👥 Community-Based Tourism
Tourism managed by local communities, ensuring benefits stay within the island and authentic cultural experiences for visitors.
💻 Digital Nomad Tourism
Islands attracting remote workers for extended stays, creating year-round tourism with less environmental impact than mass tourism.
Key Takeaways
Understanding island destinations is crucial for the study of travel and tourism:
- Islands offer unique tourism experiences due to their geographical isolation and distinctive features
- Different types of islands (tropical, volcanic, cultural) appeal to different tourist segments
- Island economies often depend heavily on tourism, creating both opportunities and vulnerabilities
- Sustainability is particularly challenging for islands due to limited resources and fragile ecosystems
- Successful island destinations balance tourism development with environmental protection and community needs
- Future trends point toward more sustainable and community-focused approaches to island tourism